Key Aspects of Flying in Greece
In this section you can view all national aviation procedures and regulations. All pilots either Greek or not are expected to comply with the following section.
Table of Contents
Units of Measurement
| To measure… | Units |
|---|---|
| …Distance | Nautical Miles and tenths |
| …Relatively short …distances | Metres |
| …Altitudes,elevation, ..height | Feet, metres |
| …Horizontal speed including wind speed | Knots |
| …Visibility and Runay Visual Range | Kilometres or metres |
| …Alimeter setting | Hectopascals |
| …Temperature | Degrees Celsious |
| …Weight | Metric tonnes or Kilogrammes |
| …Time | Hours and minutes |
Airspace Structure and Classification
2.1 Athinai FIR/Hellas UIR is divided in lower (up to FL245) and upper airspace (up to FL660).
2.2 The airspace of ATHINAI FIR / HELLAS UIR, above FL 195 is designated as Controlled
Airspace Class C. In this airspace:
- IFR and VFR flights are permitted and all flights are provided with air traffic control service.
- IFR flights are separated from other IFR flights and from VFR flights.
- VFR flights are separated from IFR flights and receive traffic information in respect of other VFR flights.
2.3 IFR and VFR flights operating within airspace Class C shall follow ATS routes and they are subject to ATC clearance.
2.4 The airspace between FL290 and FL410 inclusive is RVSM airspace. Within RVSM airspace the vertical separation minimum shall be:
- 1000ft between:
– RVSM approved aircraft. - 2000ft between:
– non-RVSM approved aircraft and any other aircraft.
– an aircraft experiencing a communication failure.
2.5 VFR flights above FL 285 are not permitted within ATHINAI FIR / HELLAS UIR due to the implementation of RVSM.
2.6 VFR flights during night are not permitted within airspace Class C above FL 195 under any circumstances.
2.7 In any case that IFR flights are not assigned with a discrete code by the appropriate ATC unit shall operate the transponder on Mode A 2000 and Mode C.
2.8 In any case that VFR flights are not assigned with a discrete code by appropriate ATC unit shall operate the transponder on Mode A 7000 and Mode C.
2.9 For IFR and VFR flight, cruising flight levels should be planed following the WestEven-EastOdd Rule
Air Traffic Services
The ATS services provided to aircraft operating within ATHINAI FIR / HELLAS UIR, are the following:
a) Air Traffic Control Services (ATC):
- Area Control – ACC,
- Approach Control – APP,
- Aerodrome Control – TWR,
- RADAR,
b) Flight Information Services (FIS):
- Flight Information Service (FIS) for en-route and terminal traffic,
- Automatic Terminal Information Service (ATIS),
- Aerodrome Flight Information Service (AFIS)
At IVAO, en-route Air Traffic Services are provided by Athinai ACC (LGGG_CTR) and Makedonia ACC (LGMD_CTR) up to FL660 inclusive.
In the absence of online local ATS stations (GND, TWR, APP, etc.), aerodrome and TMA, Air Traffic Services are provided by the respective ACC units.
Communications
Pilots flying within controlled airspace with an online ATS unit are required to contact the controller upon his request or before entering his area of control. In case of no online ATC station in the area, pilots should transmit their intentions on the UNICOM frequency 122.800.
VFR
5.1 VMC Minima
5.2 VFR flights regulations
- For the conduct of a VFR flight, Visual meteorological conditions should prevail.
- VFR flights operate during daytime. Daytime is considered the period between 30 minutes before sunrise until 30 minutes after sunset.
- VFR flights above FL195 are prohibited unles the appropriate ATS unit is online and approval has been granted.
- VFR flights operating at and below FL 195 are uncontrolled flights and are provided only with FIS. Terrain and obstacles clearance rest with the pilot.
- Within CTRs and controlled ATZs VFR flights are always considered as Controlled Flights
- VFR flights in level cruising flight when operated above 3000 FT from the ground or water until FL 195 shall be conducted at a flight level appropriate to the track as specified in the table of cruising levels, except where otherwise indicated in air traffic control clearances or specified for flights within controlled airspace.
- VFR Flights within controlled airspace, are required to follow the published VFR routes and altitude restrictions when such are published.
5.3 Change from VFR to IFR
5.3.1 In flight:
In case of no VMC and when the Special VFR is not possible the pilot must inform ATC and request a clearance to continue his flight according IFR. If unable to continue as IFR flight, he should land as soon as practicable.
5.3.2 The change of flight rules is planned before the flight:
When item 8 (Flight Rules) is Z (VFR changing to IFR), then in item 15 (Route) you must specify from what point the flight will become IFR, as well as the speed and the planned level.
5.4 VFR squawk codes
- VFR flights operating at FL 195 and below shall operate the transponder on Mode A/3.
- Code 7000 and Mode C. A discrete transponder code may be assigned for flight monitoring.
5.5 Special VFR
5.5.1 Special VFR flights may be authorized within a CTR, when ground visibility is not less of than 1500 M (ceiling not less than 1500 FT) and traffic conditions permit, subject to the approval the unit providing approach control service.
5.5.2 Standard IFR separation is provided between all IFR flights and special VFR flights and between all special VFR flights. Terrain and obstacles clearance rest with the pilot.
IFR
6.1 Reduced vertical separation minimum (RVSM)
6.1.1 HELLAS UIR is a part of the “EUR RVSM airspace”.
6.1.2 RVSM shall be applicable in part of that volume of Greek airspace between FL 290 and FL 410 inclusive
6.2 Change from IFR Flight to VFR Flight
6.2.2 An aircraft electing to change the conduct of its flight from compliance with the instrument flight rules to compliance with the visual flight rules shall notify the appropriate air traffic services unit specifically that the IFR flight plan is cancelled and communicate thereto the changes to be made to its current flight plan.
6.2.3 Change from instrument flight rules (IFR) flight to visual flight rules (VFR) flight is only acceptable when a message initiated by the pilot-in-command containing the specific expression “CANCELLING MY IFR FLIGHT”, together with the changes, if any, to be made to the current flight plan, is received by an air traffic services unit.
6.3 Selection of flight level and cruising altitudes.
- An IFR flight shall be flown at a level which is not below the minimum established flight
- Altitude or where no such minimum flight altitude has been established:
a) Over high terrain or in mountainous areas, at a level which is at least 2000ft above the highest obstacle located within 8km of the estimated position of the aircraft.
b) Elsewhere, at a level which is at least 1000ft above the highest obstacle located within 8km of the estimated position of the aircraft.
6.4 SSR operation and Transponders
6.4.1 All IFR flights will be assigned a discrete squawk code by the appropriate ATC unit. If no ATC is online, all IFR flights should squawk 2000.
6.4.2 While on ground transponders must be switched off, in order to avoid undesirable transponder replies.
6.4.3 Switch transponder “on” immediately after receiving clearance for take-off.
Radar Services
7.1 Area Radar Service is provided within ATHINAI FIR / HELLAS UIR by ATHINAI ACC – call sign: ATHINAI RADAR and MAKEDONIA ACC – call sign: MAKEDONIA RADAR
7.2 Approach Radar Service is provided within ATHINAI TMA, as well as within THESSALONIKI TMA, RODOS TMA, IRAKLION TMA and KERKIRA TMA, by the respective APP unit.
7.3 Positive identification must be established by the Radar operator immediately after the establishment of radio contact with the Radar unit.
Special Requirements and Regulations
8.1 All VFR and IFR traffic should check for an active ATC position in the Greek airspace before starting the engines.
8.2 Taxi without any clearance is allowed only when there is no active ATC position for the relevant airport or no Athens or Makedonia Control is online. In this case, all intentions should be transmitted in the UNICOM frequency 122.800
8.3 Text using pilots first execute and than readback the instructions.
8.4 The primary language for communication between pilot and ATC is English and the secondary is Greek.
Athens El. Velizelos airport(LGAV) Runway preferential System
Runways 03R/L are used unless the tailwind component exceeds 5 knots or the runway surfaces are wet. In that case Runway 21R is used for arrivals and 21L for departures. In case runways 03R/L are used then
Time Period Take-Off Runway Landing Runway
- 07:00-15:00 03R 03L
- 15:00-18:00 03L 03R
- 18:00-23:00 03R 03L
- 23:00-07:00 03L 03R
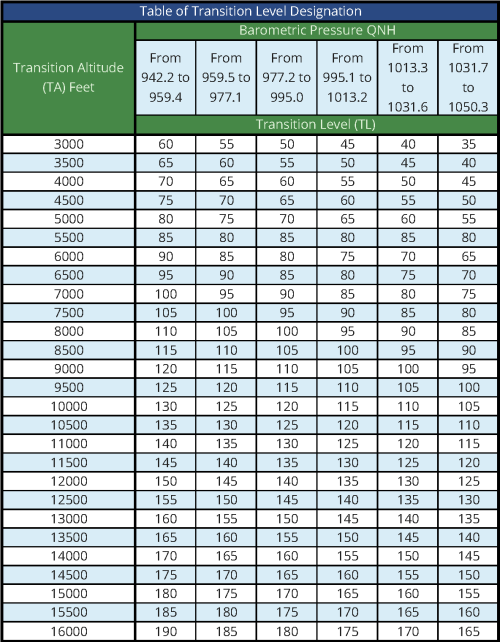
Transtion Altitude and Transition Level
10.1 In Greek airspace each airport has a fixed Transition Altitude and the Transition level is set by the controller according the following table:
Emergencies
11.1 In general, the Emergency, Unlawful Interference, Communications Failure, Interception and Search and Rescue procedures are in conformity with the Standards, Recommended Practices and Procedures in ICAO Annexes and Documents.
11.2 Some special radio communication failure procedures apply in the following area/TMAs:
11.2.1 ATHENS TMA
Aircraft under Radar Control In the event of communication failure and in the absence of previous ATC instructions, the pilot should, if unable to execute a visual approach:
– continue by own navigational means, to execute the approach he was vectored for, or
– when vectored to execute a visual approach to Elefsis airport, proceed directly to
Aigina NDB “EGN”, maintaining the last assigned altitude, if it is higher or equal to 4000ft, and execute one of the instrument approach procedures, as appropriate, without delay. Aircraft below 4000ft must proceed to “EGN” NDB making an initial climbing turn to 4000ft, taking into account high terrain and obstacles in the vicinity of the airport.
11.2.2 IRAKLION TMA
In the event of communication failure, and in absence of previous ATC instructions, the pilot-in-command shall:
a. if unable to execute a visual approach, continue by its own navigational means to execute the instrument approach he was vectored for;
b. in case he was vectored for a visual approach and still in IMC, he should proceed, by his own navigational means to “IRA” VORDME maintaining the last assigned altitude if higher or equal to 6000ft then proceed to GONSO at 3000ft and execute instrument approach to RWY 27 or as appropriate for the runway-in-use. If the last assigned altitude was below 6000ft, an initial climbing turn to 6000ft is necessary before starting the above procedure from “IRA” VORDME.
NOTE: IF “IRA” VORDME is unserviceable the pilot should make an initial climbing turn to 8500ft proceeding to “HER” NDB and execute the Lctr DME approach procedure as appropriate for the runway in use. In all cases pilots must take into account the high than terrain in the south sectors of Iraklion airport, and must not enter these sectors at an altitude less than 10000ft.
11.2.3 KERKIRA TMA
In the event of communication failure, and in absence of previous ATC instructions, the pilot-in-command should, if unable to execute a visual approach, continue by his own navigational means to execute the instrument approach he was vectored for. In the case he was vectored for a visual approach to Rwy 17/35, and still in IMC, he should proceed, by his own navigational means to “GAR” VORDME maintaining the last assigned altitude, if it is higher or equal to 4500ft and execute the “GAR” VORDME RWY 35 instrument approach appropriate for the runway-in-use.
a) aircraft below 4500ft must proceed to “GAR” VORDME, making an initial climbing turn to 4500ft, taking into account high terrain and obstacles in the vicinity of the airport.
b) in case of “GAR” VORDME is unserviceable, the pilot-in-command should use “KEK” NDB and execute the “KEK” VORDME-NDB Rwy 35 procedure.
11.2.4 MAKEDONIA TMA
In the event of complete aircraft communication failure and in the absence of previous ATC instructions, the pilot should, if unable to execute a visual approach, continue by his own navigational means to execute the instrument approach he was vectored for. If he was vectored for a visual approach and still in IMC, he should proceed by his own navigational means to ‘MKR’ VORDME maintaining the last assigned altitude, if higher or equal to 5500ft, execute the “MKR” VORDME instrument approach appropriate for the runway-in-use. If he was vectored for a visual approach to RWY 28, he should proceed to “MKR” VORDME and execute the “MKR” VORDME for RWY 34 followed by a circling approach to RWY 28.
NOTE: Aircraft below 5500ft must proceed to “MKR” VORDME, making an initial climbing turn to 5500ft, taking in account high terrain and obstacles in the vicinity of the airport. In case “MKR” VORDME is unserviceable, the pilot should use ‘TSL’ VORDME and execute “TSL” VORDME approach for RWY 34 followed by a circling approach to runway-in-use. Climb or descent either after departure, enroute or at the arrival phase at a rate not exceeding 2000ft/min. Arrange the flight so as to arrive over the most desirable navigational aid, serving the airport of intended landing at or as closely as possible to the time of arrival resulting from the current FPL. If unable to land at destination, consider the case as emergency, and handle it on ad hoc basis.
11.2.5 RODOS TMA
In the event of complete aircraft communication failure and in the absence of previous ATC instructions, the pilot should, if unable to execute a visual approach, continue by his own navigational means to execute the instrument approach he was vectored for. If he was vectored for a visual approach to runway 07 or 25, and is still in IMC, he should proceed by his own navigational means to “RDS” VORDME maintaining the last assigned altitude, if higher or equal to 6000ft, execute the instrument approach for the runway-in-use.
NOTE: Aircraft below 6000ft must proceed to “RDS” VORDME, making an initial climbing turn to 6000ft, taking in account high terrain and obstacles in the vicinity of the airport.
